uterine polyp impact blood test|round polyps in uterus : retailer An endometrial polyp is a usually noncancerous growth attached to the inner wall of the uterus, common for women undergoing or who have completed menopause. What is an endometrial polyp? Endometrial polyps are .
Empresas - TeleVía | Estar donde quieres
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Tabela Fipe Hyundai HB20 2015. O preço do carro Hyundai HB20 2015 varia de R$ 42.834 até R$ 54.300, a depender da versão. 13 Versões do HB20 2015. Clique na versão para .
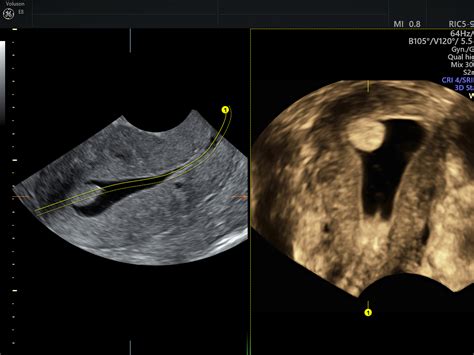
Uterine polyps are growths that occur in the inner lining (endometrium) of your uterus. They're attached to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extend inward . The following tests might be used to diagnose uterine polyps: Transvaginal ultrasound. A slender, wandlike device placed in the vagina emits sound waves and creates . Endometrial polyps are a common gynecological presentation, both in pre and postmenopausal patients. They may be identified incidentally on imaging, or patients may . Tissue growths inside the uterus can cause abnormal uterine bleeding or infertility. Learn about tests and treatment.
Uterine polyps can cause bleeding and may affect your fertility, but many women don’t have symptoms. Learn more about the causes, symptoms, complications, diagnosis, . An endometrial polyp is a usually noncancerous growth attached to the inner wall of the uterus, common for women undergoing or who have completed menopause. What is an endometrial polyp? Endometrial polyps are .
Uterine polyps are fleshy growths that appear on the inner lining of the uterus and extend into the cavity of the uterus. They are usually benign, but a small minority of them may be. Uterine polyps, often referred to as endometrial polyps, are abnormal growths that develop on the inner lining of the uterus, or endometrium. Most of these polyps are benign, .
Water Vapor Permeability Tester
A uterine (endometrial) polyp is a small, fleshy growth that can develop along the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). On average, these polyps are typically less than 1 cm. It’s. Typically, that's days 6 to 10 for most people or when you're on birth control pills. If you do the test in the luteal phase, if you do the test while you're bleeding, you might have a higher incidence of missing a polyp or, . Uterine fibroids, or leiomyomas, are the most common benign tumors in women of reproductive age. 1 Their prevalence is age dependent; they can be detected in up to 80% of women by 50 years of age . Uterine polyps can cause bleeding and may affect your fertility, but many women don’t have symptoms. Learn more about the causes, symptoms, complications, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of .
Type of polyps: Location: Symptoms: colorectal (colon) large intestine, colon, and rectum: blood in stool, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea: endometrial (uterine) Abnormal uterine bleeding affects many individuals who menstruate and can have a detrimental impact on physical and mental health. This Review discusses endometrial physiology and the causes . A uterine (endometrial) polyp is a small, fleshy growth that can develop along the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). On average, these polyps are typically less than 1 cm . It’s also .blocked blood vessels in the cervix; cervical infection; an abnormal response to increased levels of the oestrogen hormone. Uterine polyps. Uterine polyps are caused by an overgrowth of the cells in the lining of the uterus. It’s thought that oestrogen plays a role in their growth. Uterine polyps may be associated with:
Endometrial Polyps (Uterine Polyps). University of Colorado Gynecologic Oncology Department. CWH Link; Wethington SL, Herzog TJ, Burke WM, et al. Risk and predictors of malignancy in women with endometrial polyps. Advances in Pediatrics. 2011;18(13):3819-23. PubMed Link; Endometrial polyps. MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. .
The treatment for uterine polyps will depend on: a person’s symptoms; the risk of malignancy; fertility concerns; In people who are asymptomatic, the polyps may resolve without treatment. In .
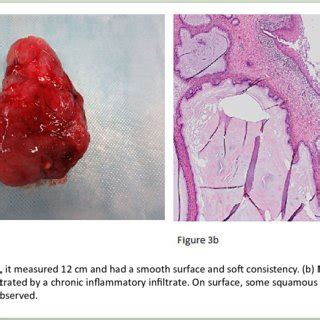
Specialized Care for Uterine Polyps. Uterine polyps develop when the lining of the uterus, or endometrium, overgrows in a particular area. Uterine, or endometrial, polyps grow from the uterus wall into the cavity and can be as small as a sesame seed or larger than a golf ball. Most uterine polyps are benign (noncancerous) but, in rare cases . Blind sampling, either through endometrial biopsy or dilation and curettage, is ineffective at diagnosing endometrial polyps, with a sensitivity of 8.4–46%. 37, 38 Microscopically, endometrial polyps are composed of a mixture of stroma, vascular channels, and glandular spaces covered by a surface epithelium. 39 A useful histologic feature in . The uterus is a pear-shaped reproductive organ that supports the development of a fetus during pregnancy. Both uterine fibroids and polyps attach to the inner wall of the uterus.Endometrial polyps are focal intrauterine endometrial neoplasm that may be single or multiple. Their size varies from few millimeters to several centimeters, and their morphology may be sessile with large or small implantation base or pedunculated . Endometrial polyps consist of three elements: endometrial glands, stroma, and blood vessels .
You may have one polyp or several. Uterine polyps can range in size from just a few millimeters to more than 6 centimeters (2.4 inches) wide. More than 95 percent of uterine polyps are benign .
Uterine polyps are growths that occur due to overgrowth of the endometrium which is the inner lining of the uterus. Learn More. . Obesity is increasingly common and has an impact on a wide range of issues in . Endometrial polyps are one of the most common etiologies of abnormal genital tract bleeding in both premenopausal and postmenopausal patients . Unlike polyps of other etiologies (eg, colon), the vast majority of endometrial polyps are neither malignant nor premalignant. However, an increased risk of malignancy occurs in selected patients (eg . Endometrial polyps are benign nodular protrusions of the endometrial surface, and one of the entities included in a differential of endometrial thickening. Endometrial polyps can either be sessile or pedunculated. . intrauterine blood clot. retained products of conception. See also. cervical polyp. tubal polyp. Quiz questions
The overall impact of HMB on daily life can be measured retrospectively with instruments like the Menstrual . In regard to laboratory tests, a complete blood count is routinely conducted to identify anemia in all patients who complain about HMB. . except for endometrial polyps and certain fibroids that can be removed efficiently by .
Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (bHCG): Low bHCG levels rule out pregnancy. Complete blood count (CBC): If you have had heavy menstrual bleeding, you may have a CBC to check for anemia. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): Women with uterine fibroids more commonly have thyroid nodules. Uterine fibroid and thyroid nodule growth are largely . Following uterine polyp removal, individuals can typically return home on the same day. . Could simple blood tests improve Alzheimer's diagnosis in the future? Damage to gut lining from ulcers .
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is a common condition that leads to increased health care costs and decreased quality of life. A systematic approach to AUB evaluation can simplify management and enhance women’s well-being. Abnormal uterine bleeding describes any variation from normal bleeding patterns in nonpregnant, reproductive-aged women beyond . Endometrial polyps, or uterine polyps, occur when cells of the inner lining of the uterus overgrow. . To perform this test, a doctor will insert a small wand into the vaginal cavity and apply . Your healthcare provider may order several tests or procedures when diagnosing abnormal uterine bleeding. These tests may include: A pregnancy test. A miscarriage causes heavy bleeding. You can test positive on a pregnancy test up to 35 days after a miscarriage. Light bleeding is also common in the early stages of pregnancy. Blood tests.
endometrial polyps in normal and infertile women raises questions regarding the role, if any, that endometrial polyps have in the pathogenesis of infertility. Impactofpolypectomy. Oneapproachtoestimatingtherela-tionship between endometrial polyps and infertility is to study the impact of polypectomy on infertile women. There
Background To investigate the impact of chronic endometritis (CE) on the recurrence of endometrial polyps (EPs) in premenopausal women after transcervical resection of endometrial polyps (TCRP). Methods This prospective study enrolled 507 women who underwent TCRP between January 1, 2022 and December 31, 2022. The patients were .
Cervical polyps are usually removed and sent for testing. In most cases, cervical polyps are benign and not a cause for concern. Advertisement. . Your cervix connects your uterus to your vagina. A polyp on your cervix is rarely cancerous; however, some polyps can change into precancers. Your healthcare provider will recommend removing a .
Uterine polyps, also called endometrial polyps, are excess outgrowths of the endometrium (innermost uterine layer) in the uterine cavity. The prevalence of polyps is estimated to be 10 percent to 24 percent of women undergoing hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) or localized endometrial biopsy. Uterine polyps are rare among women .
uterine polyps biopsy results
TeleVía gestiona 140 millones de viajes al año y más de 2.5 .
uterine polyp impact blood test|round polyps in uterus